PostgreSQL
Enables management of individual connection settings with encryption for
securely storing keys and secrets using a supplied password for symmetric key
encryption using the pgcrypto extension for PostgreSQL.
Create the Ed-Fi API Publisher Configuration Database and Table
First create the configuration database, as follows:
create database edfi_api_publisher_configuration;
Connect to the new database. Then create configuration table, as follows:
create schema dbo;
create table dbo.configuration_value
(
configuration_key varchar(450) not null
constraint configuration_value_pk
primary key,
configuration_value text,
configuration_value_encrypted bytea
);
create extension if not exists pgcrypto;
Configure API Connections
Create new API connections by executing SQL statements similar to what is shown
below. The pgcrypto functions used below employ symmetric key encryption based
on the supplied password.
For the API Publisher, the password can be supplied via the command-line using
--postgreSqlEncryptionPassword, accessed through an environment variable named
EdFi:ApiPublisher:ConfigurationStore:PostgreSql:EncryptionPassword (or
EdFi__ApiPublisher__ConfigurationStore__PostgreSql__EncryptionPassword), or
through the configurationStoreSettings.json file.
-- Insert plain text values into the 'configuration_value' column
insert into dbo.configuration_value(configuration_key, configuration_value)
values ('/ed-fi/apiPublisher/connections/Hosted_Sample_v5.2/url', 'https://api.ed-fi.org/v5.2/api/');
-- Insert encrypted values into 'configuration_value_encrypted' column
insert into dbo.configuration_value(configuration_key, configuration_value_encrypted)
values ('/ed-fi/apiPublisher/connections/Hosted_Sample_v5.2/key', pgp_sym_encrypt('RvcohKz9zHI4', 'my-secure-password'));
insert into dbo.configuration_value(configuration_key, configuration_value_encrypted)
values ('/ed-fi/apiPublisher/connections/Hosted_Sample_v5.2/secret',
pgp_sym_encrypt('E1iEFusaNf81xzCxwHfbolkC', 'my-secure-password'));
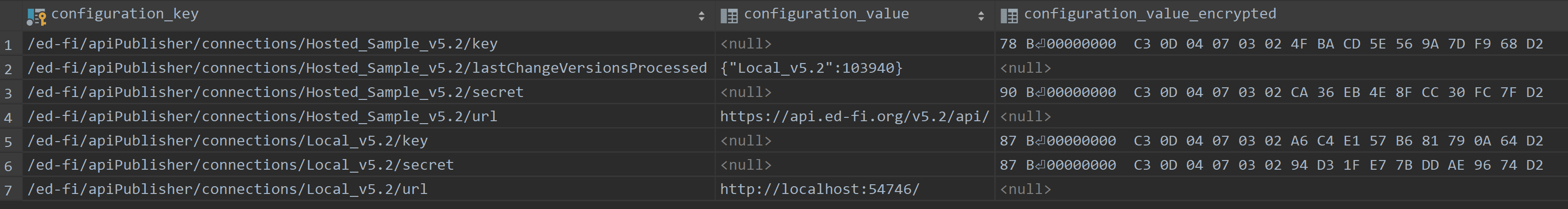
The name of the connection (Hosted_Sample_v5.2 in the example above) should
not contain spaces since a primary usage scenario is to provide the name in a
command-line argument to the utility (i.e.--sourceName=Hosted_Sample_v5.2).
Configure API Publisher
To use the PostgreSQL Configuration Store, change the provider setting in the
configurationStoreSettings.json file to postgreSql, as shown below.
{
"configurationStore": {
"provider": "postgreSql",
"postgreSql": {
"connectionString": "Host=localhost;Database=edfi_api_publisher_configuration",
"encryptionPassword": ""
}
}
}
PostgreSQL Credentials
The Configuration Store implementation uses the Npgsql driver which provides a few mechanisms for providing credentials in a more secure manner than embedding them in the connection string in the configuration file shown above.
Recommendation is to either add the Username connection string parameter into
the configured connection string above, or to set the PGUSER environment
variable to contain the user name.
Then, create a
PostgreSQL password file
to supply the password at runtime. The default location for this file is
~/.pgpass in Linux, or %APPDATA%\postgresql\pgpass.conf in Microsoft
Windows, but an explicit file path can be provided through the PGPASSFILE
environment variable.
Encryption Password
While you can set the encryptionPassword (in plain text) in the settings file
shown above, it is recommended that you manage it externally (and securely) and
supply it at runtime using either the --postgreSqlEncryptionPassword
command-line argument, or by setting it in an environment variable named
EdFi:ApiPublisher:ConfigurationStore:PostgreSql:EncryptionPassword (in Linux
use double underscores __ as the delimiter rather than :).