PostgreSQL Installation Notes
Install PostgreSQL 16.x on port 5432 if you intend to use PostgreSQL as a backing datastore for the ODS / API.
If you already have a PostgreSQL server configured with a superuser different to postgres...
In environments where PostgreSQL server was setup with a custom superuser instead of the default postgres, the Ed-Fi ODS / API database templates will fail to be restored because they require a postgres user or a user with a postgres role to exist.
For these scenarios, a postgres role can be created and assigned to the user executing the restore. This example will show how to add such role without login capabilities and assign to the custom superuser.
Prerequisites
Ensure you have:
- Custom Superuser Credentials – The username and password for the custom superuser.
- Access to the PostgreSQL Server – Via the
psqlcommand-line tool or a PostgreSQL client likepgAdmin.
Steps to Create a postgres Role
1. Connect to the PostgreSQL Server
Connect to your PostgreSQL server using the custom superuser account:
psql -U <custom_superuser> -h <host> -d <database_name>
Enter the password for <custom_superuser> when prompted.
2. Create the postgres Role
Run the following SQL command to create a postgres role without login capability:
CREATE ROLE postgres WITH NOLOGIN INHERIT;
3. Assign the postgres Role to custom superuser
Assign the role to the custom superuser (or the user you created for the EdFi ODS /API database):
GRANT <custom_superuser> TO postgres;
PostgreSQL Visualization Tool
Unlike SQL Server, PostgreSQL does not include a GUI to visualize the database (commands are executed via the command line using psql). Below is a list of various tools that work:
Install PostgreSQL
Installation of PostgreSQL can be done either using the binaries or using Docker. The recommended solution is to use the Docker install using Linux containers.
Installation using PostgreSQL Installer
Install using the PostgreSQL installer. Version 16.x is compatible with the ODS / API.
- Note the installer includes pgAdmin as an option.
- The PostgreSQL installation guide has details.
Notes while stepping through the installation wizard:
- If you want to install only the tools uncheck PostgreSQL Server, pgAdmin 4 and Stack Builder.
- Enter a password for the postgres superuser.
- Use port 5432 (default).
PostgreSQL Installation with Docker
Initial setup with Docker:
- Install Docker using this guide.
- Create a Docker Compose file.
Create a Docker Compose file (name: docker-compose.yml) to bootstrap
PostgreSQL using Linux containers. More information on the Docker Compose file
can be found on the Docker documentation
site.
services:
pg16:
image: postgres:16-alpine
container_name: pg16
volumes:
- pg16-database:/var/lib/postgresql/data
ports:
- 5432:5432
environment:
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=${PG_PASSWORD}
restart: on-failure
volumes:
pg16-database:
driver: local
name: pg16-database
Create an environment file (name: .env) to be consumed by Docker Compose. By
default the environment file needs to be in the same folder as the Docker
Compose file.
PG_PASSWORD=P@ssw0rd
Sample files for these can be downloaded from the download panel on the right.
Data Retention and Docker Compose
Once you have set up your docker compose.yml and .env files and placed them in a folder (e.g., C:\PGDockerSetup), navigate to that folder in PowerShell and run docker compose. This utility reads the docker compose.yml configuration file and runs all of the containers described in that file.
To bring up the environment:
docker compose up -d
To stop the volumes and containers, retaining data:
docker compose down
To stop the services and remove them, deleting all data:
docker compose down -v
Configure pgpass.conf
A pgpass.conf file must be set up to store passwords in a location accessible by IIS. It is required by database deployment scripts for the ODS / API. Additionally, a PGPASSFILE environment variable should be setup to specify the location of pgpass.conf file.
Create a pgpass.conf file. Note that the password should be your Postgres superuser password and if you are deploying Postgres via Docker, it should match the password in your environment file.
localhost:5432:*:postgres:P@ssw0rd
Set the environment variable PGPASSFILE to the location of the pgpass file that
was created, which is the recommended approach. Optionally, the file can be
saved in %APPDATA%/postgresql/pgpass.conf.
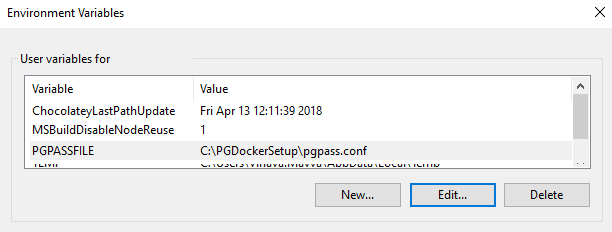
You can test the environment variable setup using:
get-item env:pgpassfile
Name Value
---- -----
PGPASSFILE C:\PGDockerSetup\pgpass.conf