Admin API 2.x - IIS Installation (Manual)
Before You Install
This section provides general information you should review before installing the Ed-Fi ODS / API Admin API for v2.2.0.
Compatibility & Supported ODS / API Versions
This version of the Admin API has been tested and can be installed for use with the Ed-Fi ODS / API v7.1. See the Ed-Fi Technology Suite Supported Versions for more details.
Prerequisites
A running instance of the ODS / API v7.1 platform must be configured and running before installing Admin API.
Admin API only supports running one instance of the application at a time in an ODS / API ecosystem. Future versions may allow for scaling and load balancing.
Admin API does not support in-place upgrades from prior versions. Please install a fresh copy of Admin API to upgrade from prior versions.
The following are required to install the Admin API with IIS:
- Enable IIS (before installing .NET Hosting Bundle).
- Install .NET 8 Hosting Bundle v8.0.21 or higher. After installing the .NET Hosting Bundle, it may be necessary to restart the computer for the changes to take effect.
Installation Steps
Installation files
The following is a Nuget package containing the Admin API v2.2.0 source files for manual deployment to IIS.
Step 1. Create Admin API Directory
Create a directory to hold all of the Admin API source files. In this example,
we'll use a directory on the following path: C:\Ed-Fi\AdminAPI.
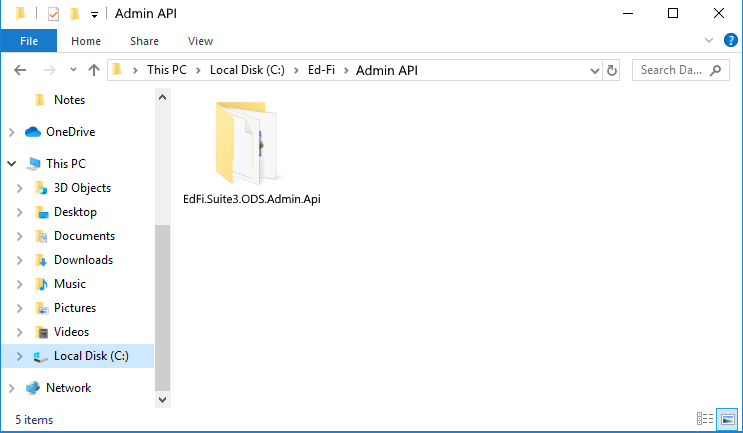
Step 2. Rename and Unzip Admin API Source Files
Download and rename the linked Nuget Package (.npkg) to .zip
Unzip the contents into the folder created in Step 1.
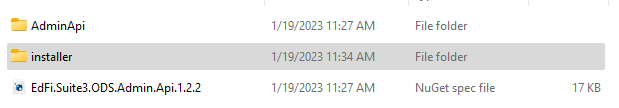
There will be two folders. AdminApi folder will have binaries. Installer folder contains PowerShell scripts required for installation.
Step 3. Ensure SQL Server Login Exists
In SQL Server Management Studio, make sure that you have a login for the database server. Guidance on how to set this up is explained in this blog post. A few basics:
- You can choose either Windows authentication or SQL Server authentication here.
- If you choose SQL Server authentication, make sure that if you have "User must change password at next login" checked. This means you must connect to SSMS with those credentials to reset the password. Otherwise, the app pools won't be able to connect.
- On the Server Roles page, ensure the "dbcreator" checkbox is checked since Entity Framework will create the database when the application is launched. You must do this when using either Windows or SQL Server authentication.
Once you have confirmed a proper SQL Server login exists, continue to the next step.
Step 4. Configure App/Web Configuration Files
You will need to manually edit connection strings, authorization settings, and
keys in AdminApi\appsettings.json. Some values to note:
- Authentication Settings
-
Authentication:SigningKeymust be a Base64-encoded 256-bit string. The following script demonstrates how to generate it, but you can use another preferred method:generate_signingkey.ps1# <base64-encoded 256-bit key>
$randomNumber = [System.Security.Cryptography.RandomNumberGenerator]::Create();
$buffer = New-Object byte[] 32;
$randomNumber.GetBytes($buffer);
[BitConverter]::ToString($buffer).Replace("-", [string]::Empty);
# Convert to base-64
$StringBytes = [System.Text.Encoding]::Unicode.GetBytes($buffer)
$Base64EncodedKey =[Convert]::ToBase64String($StringBytes)
Write-Host "Your EncryptionKey: " $Base64EncodedKey -
Authentication:AuthorityandAuthentication:IssuerUrlshould be the same URL as your application -
Changing
Authentication:AllowRegistrationtotrueallows unrestricted registration of new Admin API clients- Keeping this is flag enabled all the time is not recommended for production
-
- Change
EnableSwaggertotrueto enable generation of the Swagger UI documentation- This is not recommended for production.
- The connection strings will need to be accurately configured by the user. For more information on how to determine connection strings for your database, please reference Microsoft documentation.
- Please refer Multi-tenant Configuration for Admin API 2.x for configuring Multi-Tenant specific AppSettings and ConnectionStrings.
Here is a snippet from a properly configured application settings file:
{
"AppSettings": {
"DatabaseEngine": "SqlServer",
"PathBase": "",
"DefaultPageSizeOffset": 0,
"DefaultPageSizeLimit": 25,
"MultiTenancy": false
},
"Authentication": {
"Authority": "https://YOUR_SERVER_NAME_HERE/AdminApi",
"IssuerUrl": "https://YOUR_SERVER_NAME_HERE/AdminApi",
"SigningKey": "YOUR_BASE64_ENCODED_256_BIT_STRING",
"AllowRegistration": false
},
"SwaggerSettings": {
"EnableSwagger": false,
"DefaultTenant": ""
},
"EnableDockerEnvironment": false,
"ConnectionStrings": {
"Admin": "Data Source=(local);Initial Catalog=EdFi_Admin;Trusted_Connection=True",
"Security": "Data Source=(local);Initial Catalog=EdFi_Security;Trusted_Connection=True"
},
"Log4NetCore": {
"Log4NetConfigFileName": "log4net\\log4net.config"
},
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft": "Warning",
"Microsoft.Hosting.Lifetime": "Information"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*"
}
Step 5. Create Self-Signed Certificate in IIS Manager
This step is only necessary if you do not have a certificate from an existing ODS / API and Admin App installation in IIS.
Open IIS Manager, and double-click on "Server Certificates". Note that we must select a server/machine in the left sidebar to see this option.
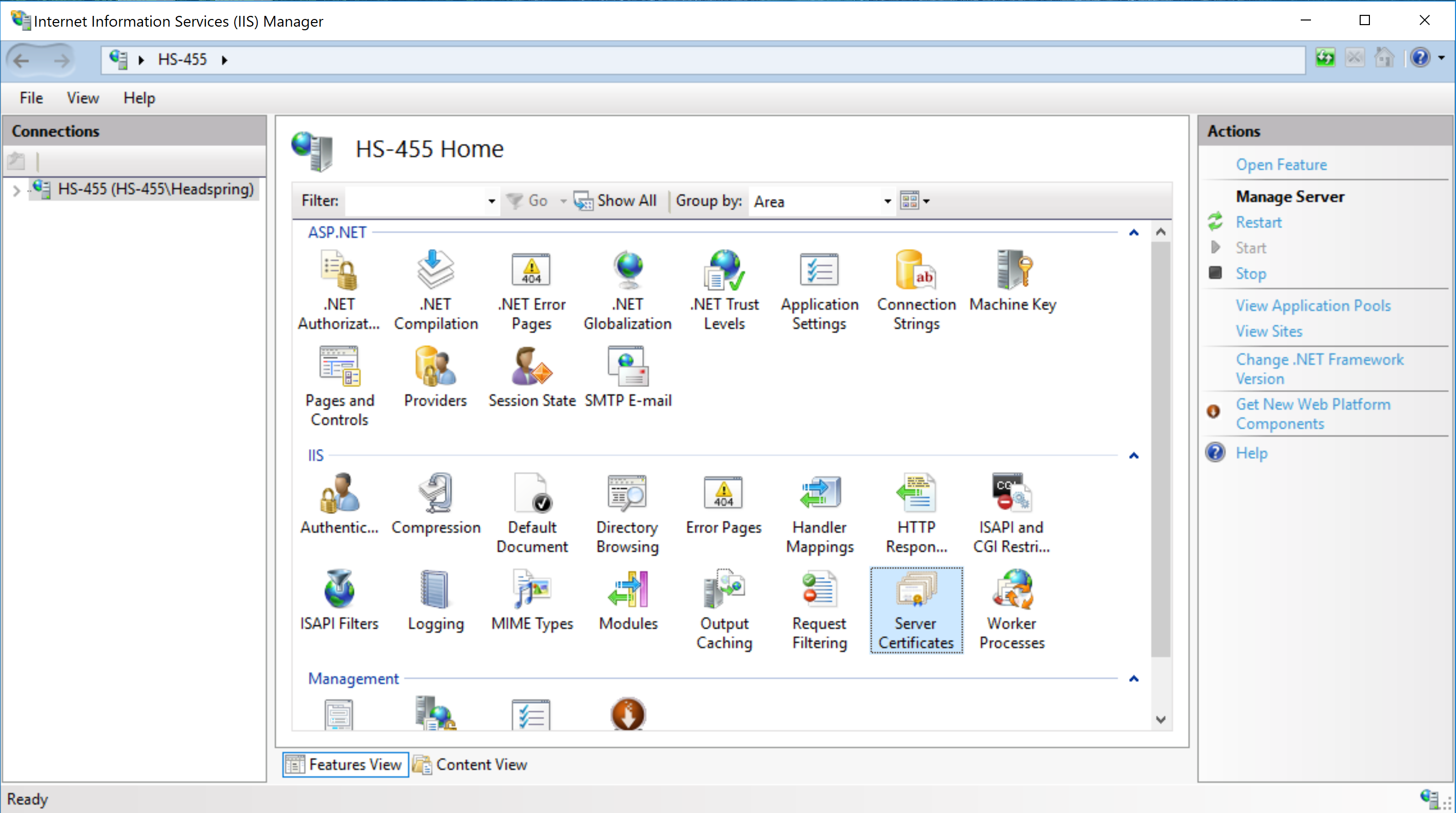
On the Server Certificate page, click on "Create Self-Signed Certificate..." on the Actions bar to the right.
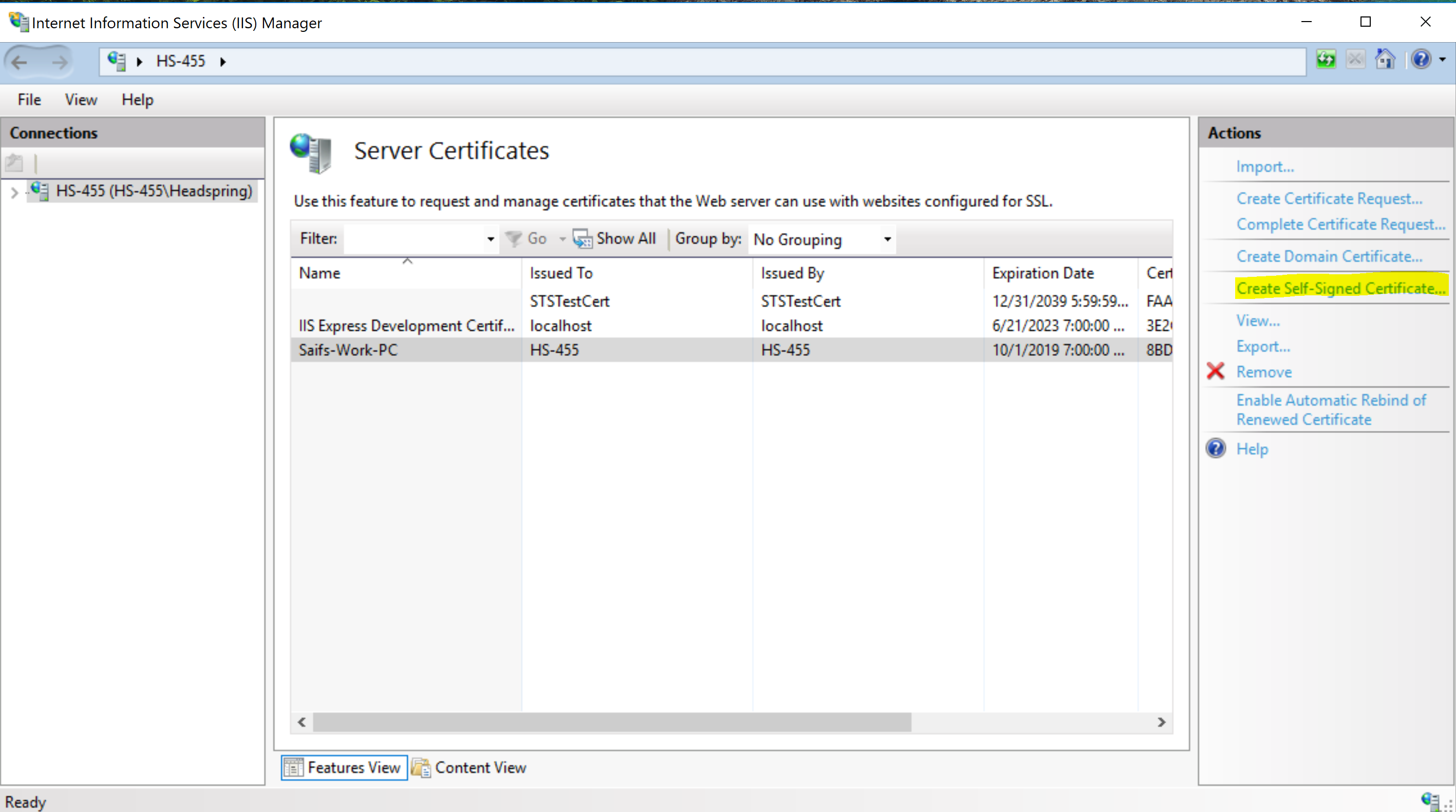
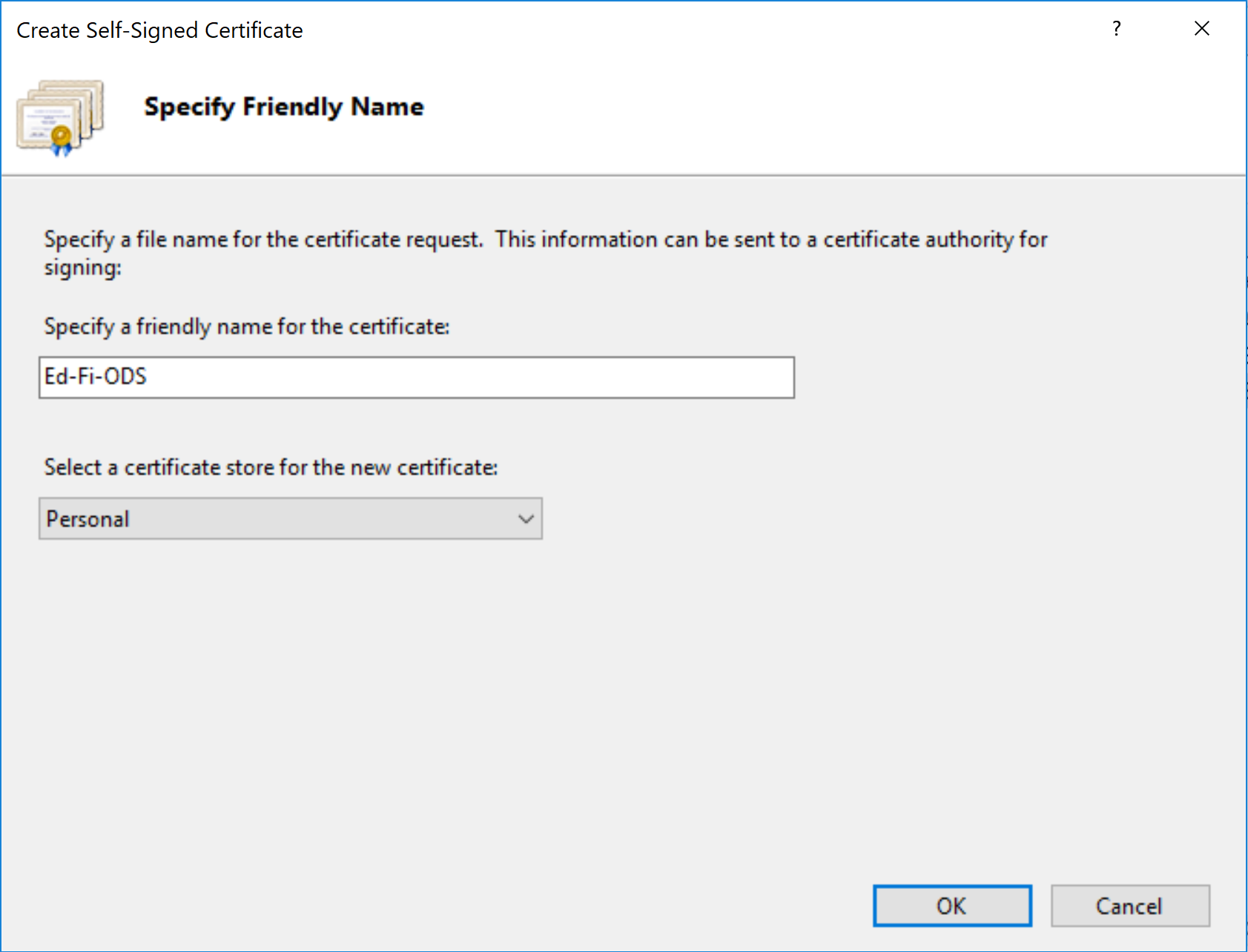
For the certificate, use "Ed-Fi-ODS" as the friendly name and make sure the certificate store is set to "Personal". Click OK. We will use this certificate in an upcoming step.
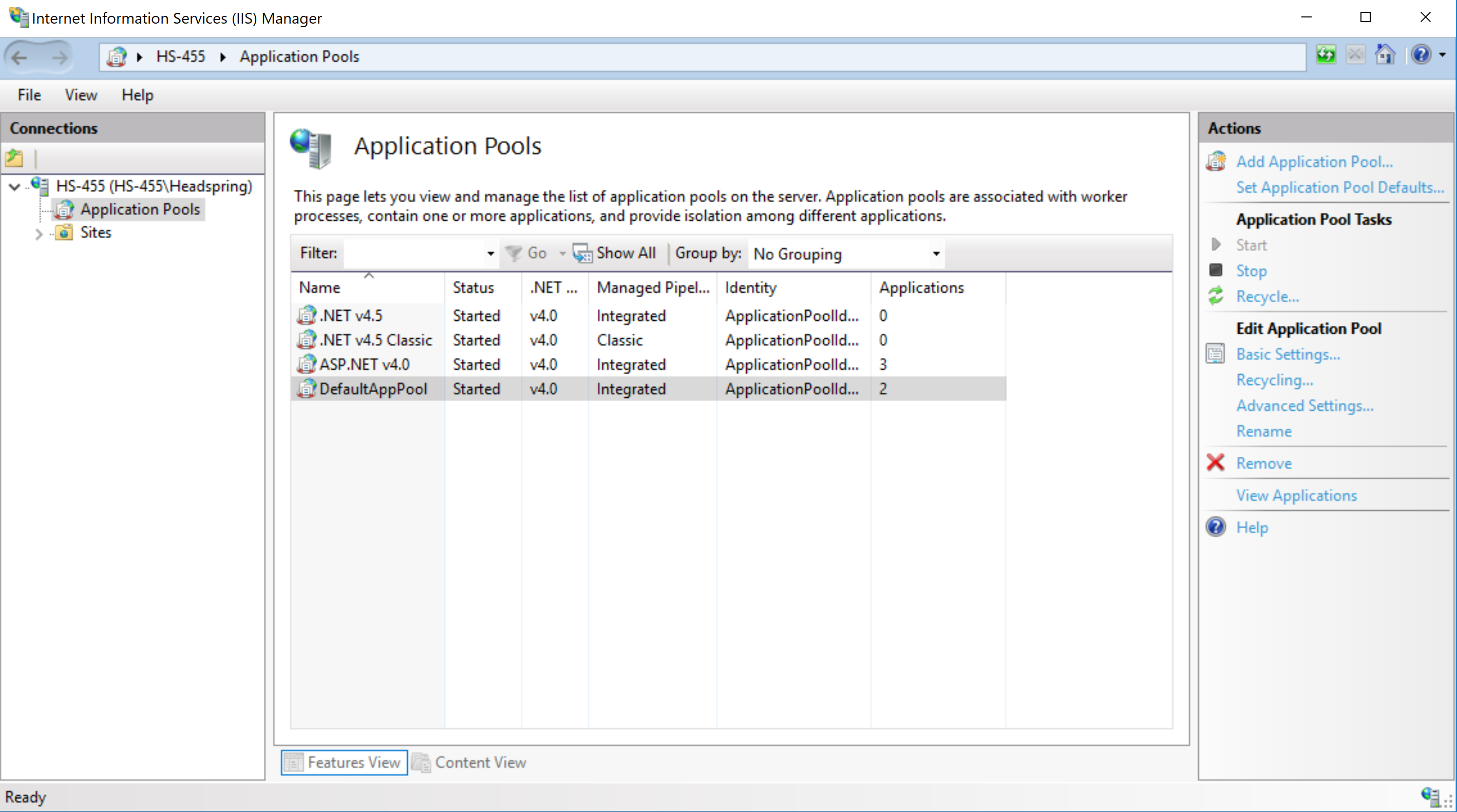
Step 6. Create Necessary Application Pools
Back in the IIS Manager main page, expand the server/machine on the left sidebar and click on Application Pools.
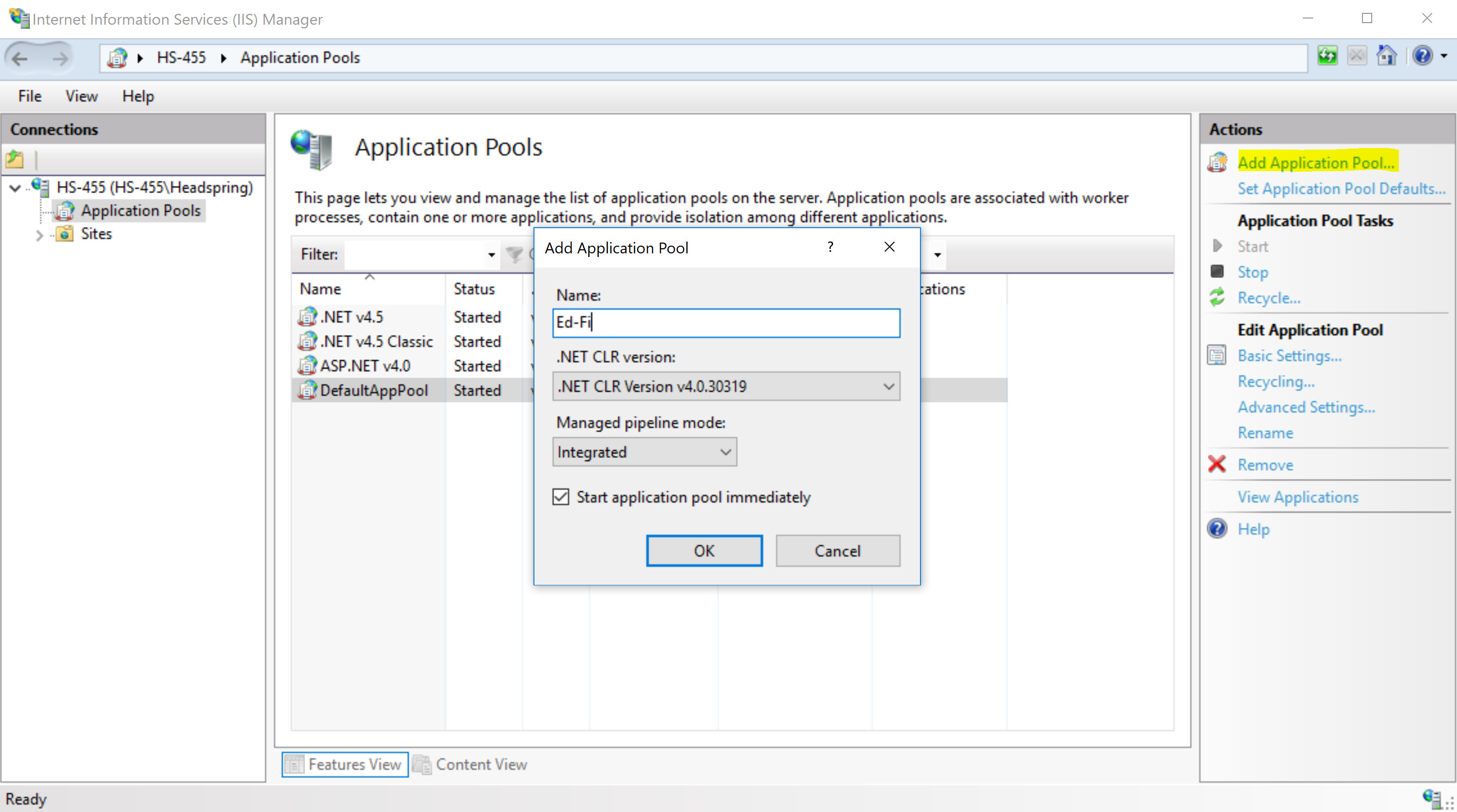
Click on "Add Application Pool..." on the Actions bar to the right, enter "Ed-Fi" as the name. Click OK.
Once that is created, click on the "Ed-Fi" application pool and select "Advanced Settings..." on the Actions bar to the right. Change the Start Mode to "AlwaysRunning".
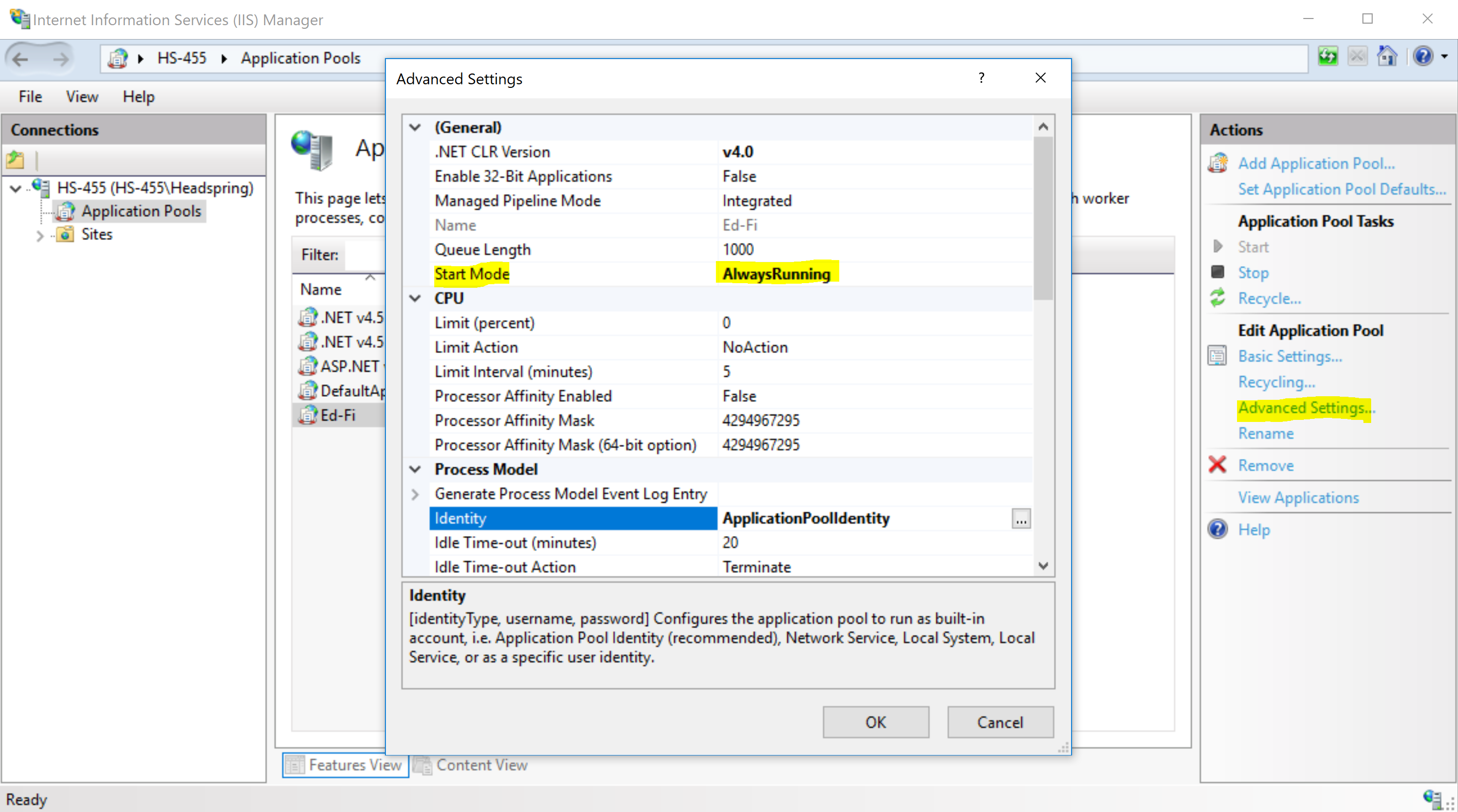
This next bit is optional if you want to use an app pool identity. If you would like to use the default "ApplicationPoolIdentity", then you can skip this section.
In the same Advanced Settings window, click on the browse icon under Process Model > Identity. Choose the custom account option and click "Set...". When setting the credentials, you can simply use the username and password that you use to log in to Windows. If you need to include the app pool domain in the username, then the username can look something like this: "localhost\username", where "localhost" is the app pool domain. Once you've entered the correct credentials, click OK on all screens until you're back to the main Application Pools page.
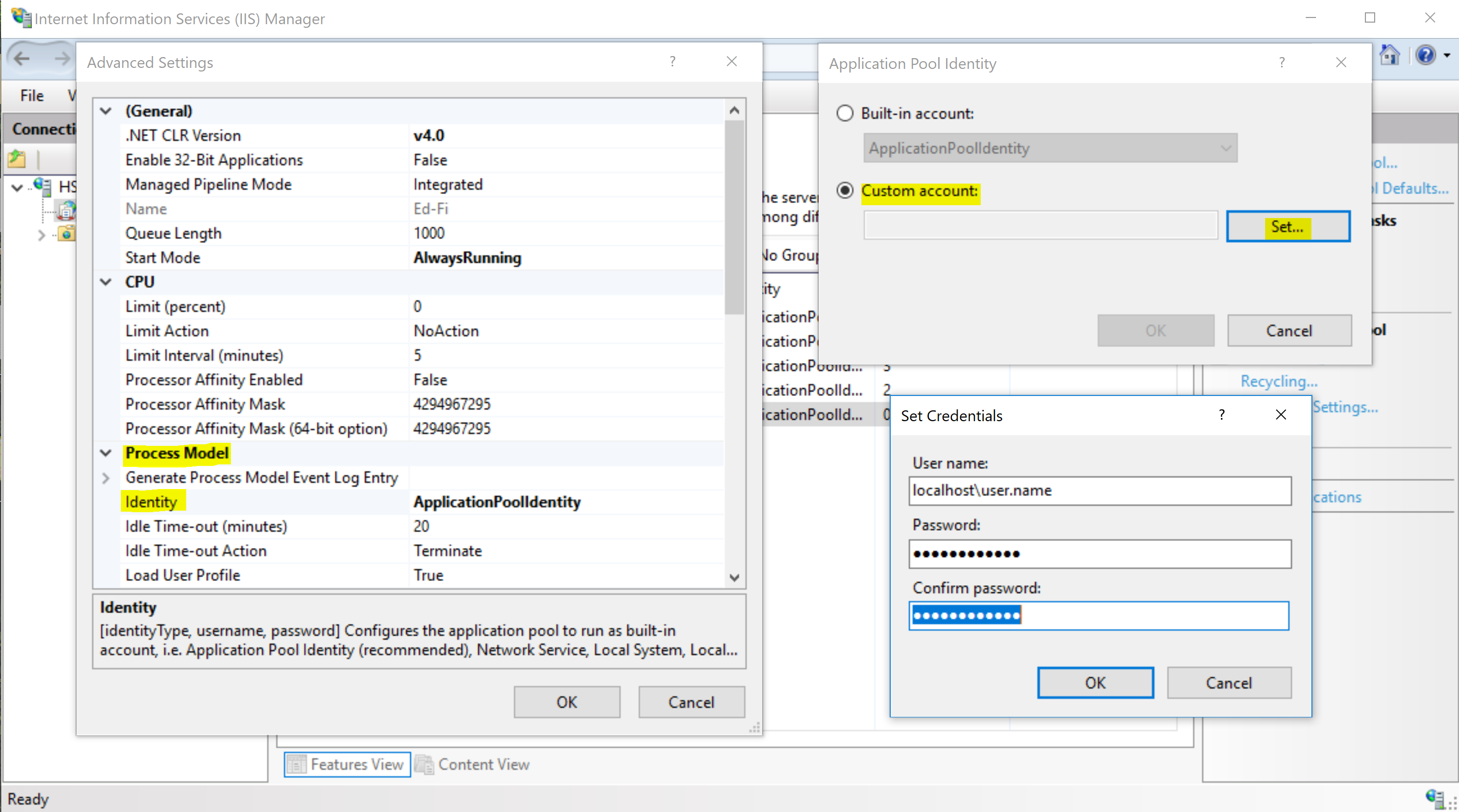
After that's done, we'll repeat the exact same steps in this section, but enter "Admin API" as the Application Pool name. We should now have 2 app pools.
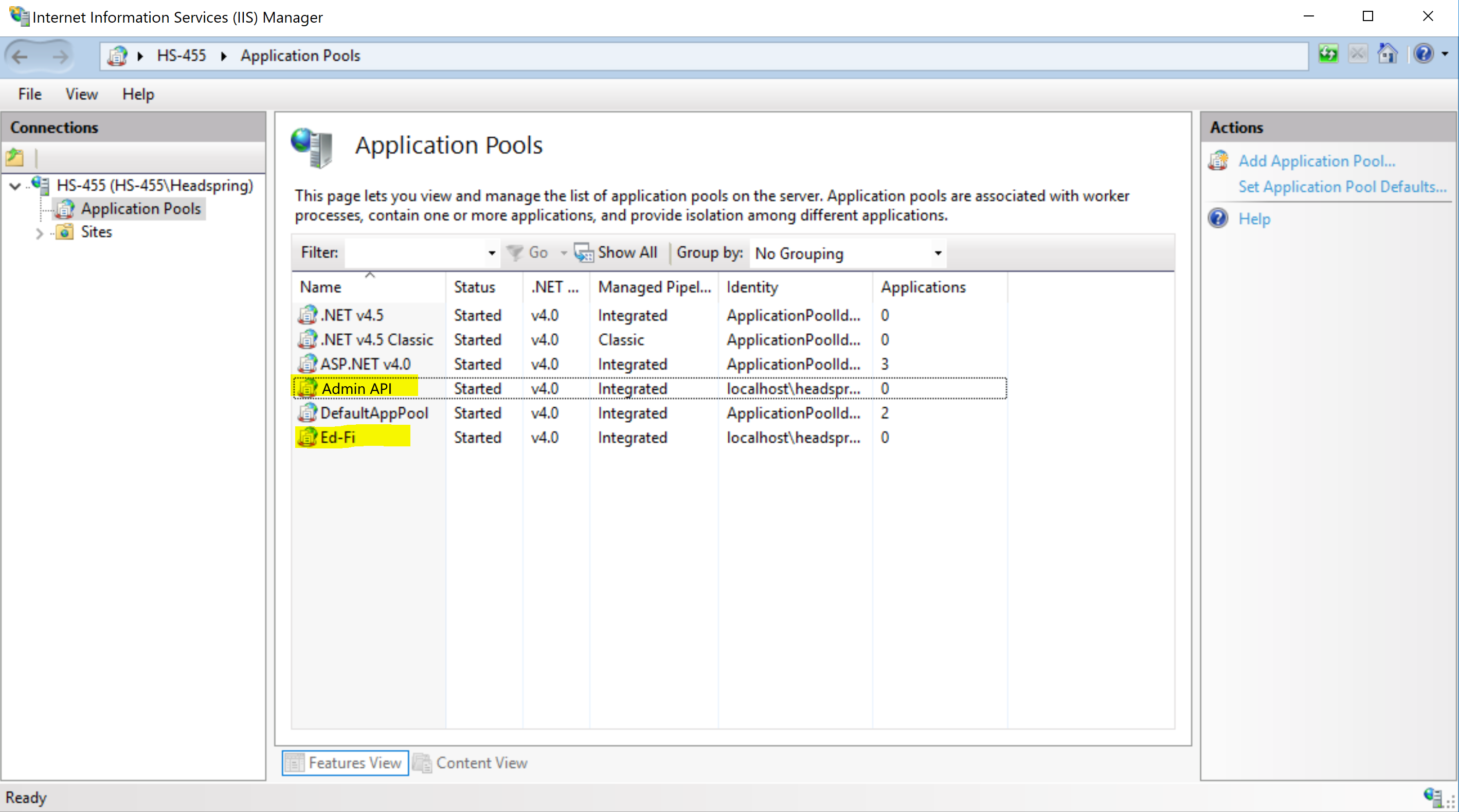
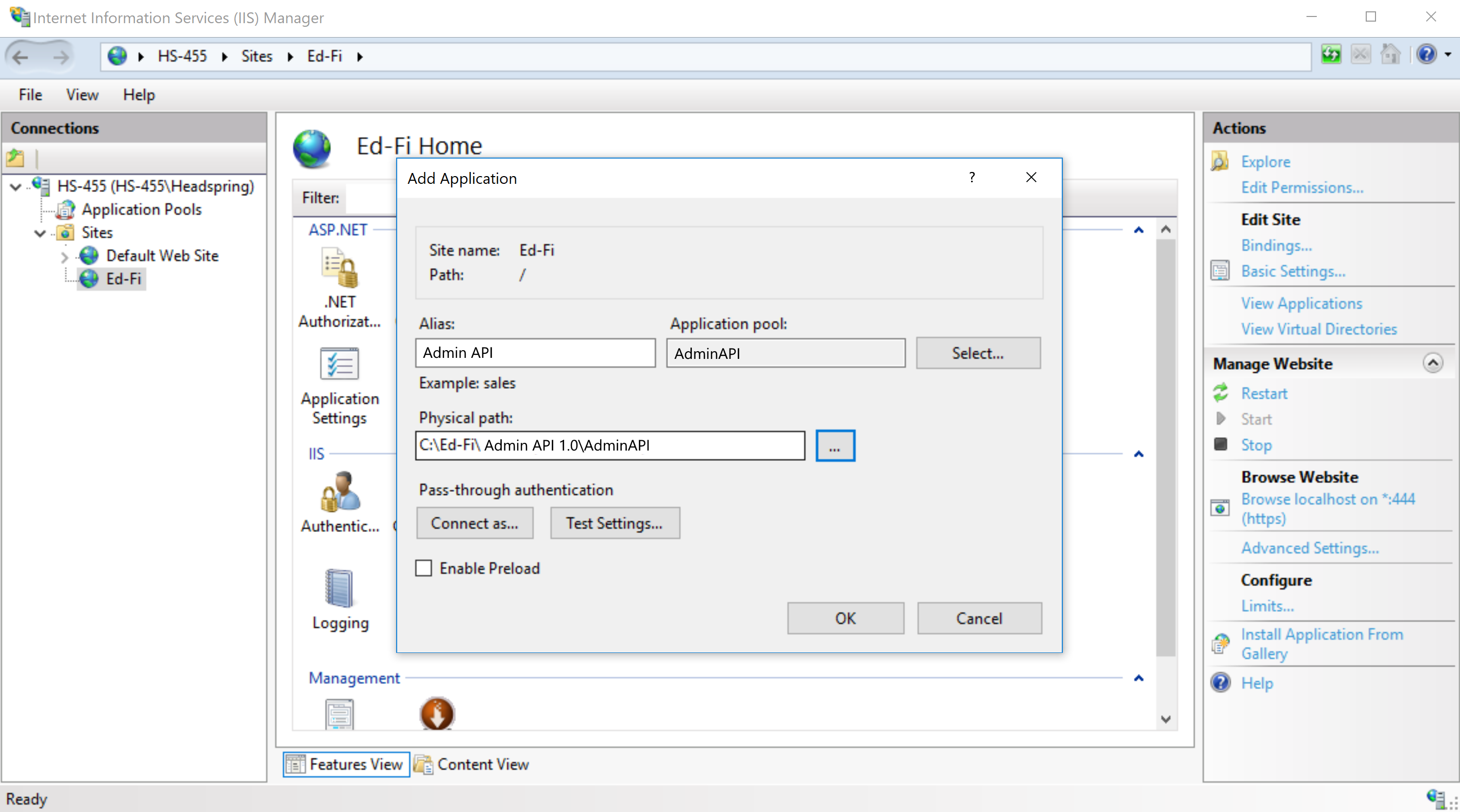
Step 8. Create Admin API Website
On the left sidebar, we'll right-click on the newly created "Ed-Fi" website, select "Add Application...", and perform the following:
- Enter "Admin API" for the Alias.
- For the Application pool, select the Admin API app pool.
- The Physical path should be set to the path of the Admin API folder (located in directory with Admin API source files).
- Hit OK.
Step 9. Initialize Admin API Database Tables
Additional tables are required for storing client authentication for Admin API, which need to be initialized manually, as shown below.
Please execute the below script against the EdFi_Admin database, using SQL Server Management Studio, Azure Data Studio, PowerShell SQL Tools, psql.exe, or PgAdmin as per your database (SQL Server or Postgres) and database tool preference.
Note: For MultiTenancy, scripts need to be executed against all the tenant specific EdFi_Admin databases( ex: EdFi_Admin_Tenant1, EdFi_Admin_Tenant2 etc..)
PostgreSQL
Execute the below script against the EdFi_Admin database using psql , PgAdmin, or the tool of your choice.
CREATE SCHEMA IF NOT EXISTS adminapi;
CREATE TABLE adminapi.Applications (
Id INT NOT NULL GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY,
ConcurrencyToken VARCHAR(128) NULL,
ClientId VARCHAR(256) NULL,
ClientSecret VARCHAR(256) NULL,
Type VARCHAR(256) NULL,
ConsentType VARCHAR(256) NULL,
Permissions VARCHAR NULL,
Properties VARCHAR NULL,
Requirements VARCHAR NULL,
DisplayName VARCHAR(256) NULL,
DisplayNames VARCHAR NULL,
RedirectUris VARCHAR NULL,
PostLogoutRedirectUris VARCHAR NULL,
CONSTRAINT PK_Applications PRIMARY KEY (Id)
);
CREATE TABLE adminapi.Scopes (
Id INT NOT NULL GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY,
Name VARCHAR(256) NULL,
ConcurrencyToken VARCHAR(128) NULL,
Description VARCHAR NULL,
Descriptions VARCHAR NULL,
DisplayName VARCHAR(256) NULL,
DisplayNames VARCHAR NULL,
Properties VARCHAR NULL,
Resources VARCHAR NULL,
CONSTRAINT PK_Scopes PRIMARY KEY (Id)
);
CREATE TABLE adminapi.Authorizations (
Id INT NOT NULL GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY,
ConcurrencyToken VARCHAR(128) NULL,
ApplicationId int NOT NULL,
Scopes VARCHAR NULL,
Subject VARCHAR(256) NULL,
Status VARCHAR(256) NULL,
Properties VARCHAR NULL,
CreationDate TIMESTAMP NULL,
CONSTRAINT PK_Authorizations PRIMARY KEY (Id),
CONSTRAINT FK_AuthorizationsId_ApplicationId FOREIGN KEY (ApplicationId) REFERENCES adminapi.Applications (Id) ON DELETE RESTRICT
);
CREATE TABLE adminapi.Tokens (
Id INT NOT NULL GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY,
ConcurrencyToken VARCHAR(128) NULL,
ApplicationId int NULL,
AuthorizationId int NULL,
Type VARCHAR(256) NULL,
CreationDate TIMESTAMP NULL,
ExpirationDate TIMESTAMP NULL,
RedemptionDate TIMESTAMP NULL,
Payload VARCHAR NULL,
Properties VARCHAR NULL,
Subject VARCHAR(256) NULL,
Status VARCHAR(256) NULL,
ReferenceId VARCHAR(256) NULL,
CONSTRAINT PK_Tokens PRIMARY KEY (Id)
);
SQL Server
Execute the below script against the EdFi_Admin database using SQL Server Management Studio, Azure Data Studio, PowerShell SQL Tools, or the tool of your choice.
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM sys.schemas WHERE name = 'adminapi')
BEGIN
EXEC( 'CREATE SCHEMA adminapi' );
END
CREATE TABLE adminapi.Applications (
[Id] int identity NOT NULL,
[ConcurrencyToken] NVARCHAR(128) NULL,
[ClientId] NVARCHAR(256) NULL,
[ClientSecret] NVARCHAR(256) NULL,
[Type] NVARCHAR(256) NULL,
[ConsentType] NVARCHAR(256) NULL,
[Permissions] NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
[Properties] NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
[Requirements] NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
[DisplayName] NVARCHAR(256) NULL,
[DisplayNames] NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
[RedirectUris] NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
[PostLogoutRedirectUris] NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
CONSTRAINT PK_Applications PRIMARY KEY (Id)
);
CREATE TABLE adminapi.Scopes (
[Id] int identity NOT NULL,
[Name] NVARCHAR(256) NULL,
[ConcurrencyToken] NVARCHAR(128) NULL,
[Description] NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
[Descriptions] NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
[DisplayName] NVARCHAR(256) NULL,
[DisplayNames] NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
[Properties] NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
[Resources] NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
CONSTRAINT PK_Scopes PRIMARY KEY (Id)
);
CREATE TABLE adminapi.Authorizations (
[Id] int identity NOT NULL,
[ConcurrencyToken] NVARCHAR(128) NULL,
[ApplicationId] int NOT NULL,
[Scopes] NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
[Subject] NVARCHAR(256) NULL,
[Status] NVARCHAR(256) NULL,
[Properties] NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
[CreationDate] DATETIME NULL,
CONSTRAINT PK_Authorizations PRIMARY KEY (Id),
CONSTRAINT FK_AuthorizationsId_ApplicationId FOREIGN KEY ApplicationId) REFERENCES adminapi.Applications (Id) ON DELETE NO ACTION,
);
CREATE TABLE adminapi.Tokens (
[Id] int identity NOT NULL,
[ConcurrencyToken] NVARCHAR(128) NULL,
[ApplicationId] int NULL,
[AuthorizationId] int NULL,
[Type] NVARCHAR(256) NULL,
[CreationDate] DATETIME NULL,
[ExpirationDate] DATETIME NULL,
[RedemptionDate] DATETIME NULL,
[Payload] NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
[Properties] NVARCHAR(MAX) NULL,
[Subject] NVARCHAR(256) NULL,
[Status] NVARCHAR(256) NULL,
[ReferenceId] NVARCHAR(256) NULL,
CONSTRAINT PK_Tokens PRIMARY KEY (Id)
);
Step 10. Execute First-Time Configuration
Continue on to First-Time Configuration for Admin 2.x.